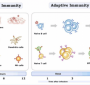
“Immunity” refers to the body’s way of getting rid of infections. Pathogens or infectious organisms carry specific antigens which cause disease. Antigens can be warded off by antibodies produced by or introduced into the body. To picture it clearly, you may think of antigens as the criminals and antibodies as the police. In this article, the two types of immunity, active and passive, will be differentiated.
Summary Table
| Active Immunity | Passive Immunity |
| Antibodies are produced by the body | Antibodies are introduced to the body |
| Takes time to have an effect | Immediate effects |
| Long-term or lifetime immunity | Short-term immunity |
Definitions
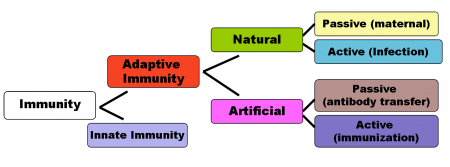
Active immunity refers to the type of immunity wherein the body produces antibodies to fight off antigens. This kind of immunity can be naturally occurring, such that when a person acquires an infection, the body produces antibodies to ward off the antigen it contains. It can also be artificially introduced through vaccination which contains killed or attenuated antigens that are weak enough not to cause the actual disease. Active immunity, through routine vaccinations, is offered to babies and children to prevent certain infections.
The antibodies take time before they actually work but once they do they are long-term – sometimes lifelong. The person becomes immune to that specific antigen and the next time it attacks the body, the immune system immediately recognizes the antigen through memory B cells. Then the body will produce antibodies that will readily fight off the infection so the person will not get sick.
Passive immunity refers to the type of immunity wherein antibodies are directly passed on or administered into the body. It can be naturally acquired during pregnancy where maternal antibodies are passed into the fetal blood through the placenta. It can also be artificially acquired through administration of immunoglobulin, which contains antibodies not produced by the body. An example is rabies immune globulin, which can be given to a patient who was bitten by a stray dog.
The antibodies introduced in the body for passive immunity are readily functional but the effect can only be temporary. The antibodies will fight off the infection immediately but do not offer lifetime immunity like active immunity does. It will only last for a few weeks or months.
Active Immunity vs Passive Immunity
What’s the difference between active immunity and passive immunity? The main difference is in how antibodies were introduced into the body. In active immunity, the body produces its own antibodies while in passive immunity, antibodies are directly administered to the body.
Active immunity offers long-term or even lifetime protection while passive immunity is only effective for a short period of time. The effect of passive immunity is immediate; however, it takes time for active immunity to do its job in fighting off infection.
Video
This video illustrates the difference between active and passive immunity.