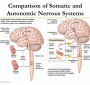
Your nervous system is the center of your body’s command. It is a smart, strong, and intelligent brain that controls all your movements, your thoughts, and the automatic responses that you have to the world around you. They also regulate other parts of our bodies and processes, including digestion, breathing, and sexual development.
| Afferent | Efferent |
| The sensory side of the nervous system. | The motor side of the nervous system. |
| Carry information to the central nervous system. | Carry information from the central nervous system. |
| Have cell bodies in the spinal cord. | Have cell bodies connected to one large axon, and there are neuromuscular junctions with the effector organs. |
Afferent and efferent are two terms which are often used in the context of the nervous system. The former term refers to sensory input while the latter term refers to the motor output.
For example, afferent nerves carry information from the sense organs to the central nervous system whereas efferent nerves carry information from the central nervous system to effector organs. Afferent nerves carry information that initiates an action while efferent nerves carry information that carries out an action.
The afferent nerve is the sensory side of the nervous system that stimulates movement. The efferent nerves are the motor side of the nervous system that controls movement. The afferent nerves are also called primary or somatic nerves.
Afferent nerves carry information that is normally transmitted to the brain via the peripheral nervous system. Afferent neurons have their cell bodies in the dorsal ganglia of the spinal cord.
The efferent nerves carry information from the central nervous system. The cell bodies of the efferent neuron are connected to one large axon, and there are neuromuscular junctions with the effector organs. There are two kinds of motor neurons, upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons.
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary functions, such as heart rate and blood pressure. Vagus nerve–the longest nerve in the autonomic nervous system–stimulation is a type of acupuncture used to treat various medical conditions. It is also called vagal nerve stimulation because this part of the nervous system controls the activity of the other two parts, the sympathetics and parasympathetics.
Afferent nerves carry information from the brain to the body, and they are sometimes called sensory nerves. The efferent nerves carry information from the body to the brain, and they are sometimes called motor nerves.
Afferent fibers usually carry impulses that travel in a direction from the periphery to central nervous system (CNS). Efferent fibers usually carry impulses from the brain to the periphery.
Afferent fibers are often called somatic nerves, and efferent nerves are called autonomic nerves. In some cases, these terms are used interchangeably.