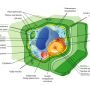
There are many different types of organisms in the world, but they can be grouped into three categories: eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and archaea. Bacteria are a type of prokaryote, but there are some differences between archaea and bacteria. For example, the archaea is not necessarily a type of bacteria, but the archaea and bacteria have a lot in common. Both are single-celled organisms that are important to life on Earth. So what are the other differences between archaea and bacteria?
The article will focus on the archaea and bacteria, the difference between archaea and bacteria, and how they interact with each other.
- 1 Summary Table:
- 2 Definitions:
- 3 Archaea Vs. Bacteria:
- 3.1 1. The cell structure
- 3.2 2. The cellular location
- 3.3 3. The motility
- 3.4 4. The food source
- 3.5 5. The chemical reactions
- 3.6 6. The habitat
- 3.7 7. The genetics
- 3.8 8. Reproduction
- 3.9 9. Virulence
- 3.10 10. The response to stress
- 3.11 11. The life cycle
- 3.12 12. The metabolism
- 3.13 13. The genome size
- 3.14 14. The taxonomy
- 3.15 15. The life span
- 3.16 16. The number of species
Summary Table:
| Archaea | Bacteria |
| A form of bacteria but is a different species of its own | A microorganism that belongs to the kingdom of Eubacteria |
| Can only live for 30 to a few hours | Can live for 10 to 15 hours |
| Not really harmful to humans | Is the cause of many diseases |
Definitions:
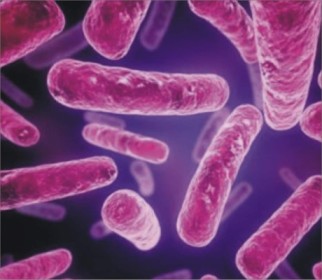
What Is Archaea?
As mentioned above, archaea are not necessarily a bacteria, but a form of bacteria that are in a different kingdom than bacteria. They are the oldest life forms on Earth and are extremophiles. They live in extreme environments, such as high temperatures and high pressures. Archaea were discovered in the 1970s by Carl Woese, a microbiologist at the University of Illinois. Archaea were originally classified as bacteria, but are now classified as their own domain in the tree of life.
What Is Bacteria?
Bacteria are a form of microorganism that can be found almost anywhere on Earth. They are single-celled organisms that are prokaryotes, meaning they do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Most bacteria are unicellular, but some can form chains or even colonies of cells. There are three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya (plants and animals). All living things can be placed into one of these three domains except for one: bacteria. Bacteria make up most of the living things on Earth and they are everywhere. In fact, if you take all the DNA from all living things on Earth and put it together, only about 1% will be human DNA. There is about 100 times more bacterial DNA than human DNA.
What is the symbiotic relationship between archaea and bacteria?
A symbiotic relationship is when two organisms live together in a mutually beneficial relationship. In the case of bacteria and archaea, the bacteria live inside the archaea and provide it with nutrients and the archaea provides the bacteria with a home. The bacteria do not use oxygen, but they do provide energy to the archaea. The archaea will then use this energy to produce ATP, which is an energy molecule that all living things need to survive. The archaea uses this ATP to make its own food, which is similar to how plants make their own food. This symbiotic relationship has existed for billions of years and continues today.
Archaea Vs. Bacteria:
There are many differences between Archaea and Bacteria. Here are some of them:
1. The cell structure
The cell structure is different in both. Bacteria are Gram-negative bacteria and have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan, which is located outside the cytoplasmic membrane. Archaea are Gram-positive bacteria and do not have a cell wall. They have an outer membrane that separates the cytoplasm from the outside environment.
2. The cellular location
The cell is found in two different locations: free-living (not attached to other cells) and in association with other cells. Bacteria are found in association with other cells. Archaea are free-living and do not attach to other cells.
3. The motility
Bacteria are not motile, while archaea can move around freely. They use flagella or cilia to move around.
4. The food source
Bacteria eat anything organic, while archaea can only digest certain materials like sugars and starch. Bacteria need oxygen to survive, while archaea do not need oxygen to survive.
5. The chemical reactions
Bacteria can carry out many different chemical reactions, while archaea can only carry out a few. They are more limited in their chemical reactions than bacteria.
6. The habitat
Archaea are found in almost every habitat on Earth. Bacteria live in a wide variety of habitats on Earth, but mostly in water and soil.
7. The genetics
Bacteria have one circular chromosome, while archaea have one linear chromosome. The bacteria also have plasmids that contain extra genes. Archaea do not have plasmids, and they do not carry out horizontal gene transfer like bacteria do.
8. Reproduction
Bacteria reproduce asexually by binary fission, while archaea reproduce sexually through the process of conjugation.
9. Virulence
Archaea are usually not harmful to humans, while bacteria can cause many diseases in humans. Bacteria are the main cause of many diseases such as strep throat, pneumonia, gonorrhea, and syphilis.
10. The response to stress
Bacteria can enter a dormant state called endospore formation when they are under stress. Archaea cannot enter this state.
11. The life cycle
Bacteria are unicellular, while archaea are usually multicellular. Archaea have more cells than bacteria do.
12. The metabolism
Bacteria use a variety of different metabolic pathways to carry out different chemical reactions, while archaea use fewer metabolic pathways. Bacteria use both aerobic and anaerobic respiration, while archaea only use anaerobic respiration.
13. The genome size
The genome size of bacteria is usually about 5 to 6 million base pairs, while the genome size of archaea is usually about 1.5 to 2 million base pairs.
14. The taxonomy
The bacterial domain is called the Bacteria, while the archaeal domain is called the Archaea. Both domains are in the kingdom of Eubacteria.
15. The life span
Bacteria have a short life span of about 30 minutes to a few hours, while archaea have a longer life span of about 10 to 15 hours.
16. The number of species
There are more than 4,000 species of bacteria, while there are less than 300 species of archaea.