It can be difficult to determine the sex of a juvenile turtle since its reproductive organs are not exposed. If you own a young turtle, you may have to wait for several years for it to mature before you can discern if it is a Jane or a Joe. Upon maturity, you can take your pet turtle to an expert to ascertain its gender. However, there are simple ways to do it yourself. How is a male turtle different from a female turtle? The difference between the two will be discussed in this article.
Summary Table
| Male Turtle | Female Turtle |
| Small and light | Big and heavy |
| Bright-colored | Dark-colored |
| Has long nails on front feet | Has short nails |
| Has a long, thick, and flat tail | Has a short tail |
| Its cloaca is near the end of the tail | Its cloaca is close to the body |
| Its butt is on the edge of the tail | Its butt is not exposed |
| Has a concave plastron | Has a convex plastron |
| Not capable of laying eggs | Capable of laying eggs |
Descriptions
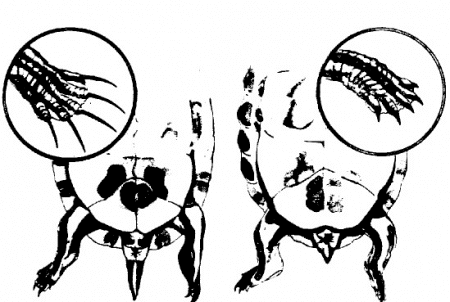
Although it depends on the species of the turtle, a male turtle generally has a long, thick and flat tail to contain its reproductive organ. Its cloaca, which is the opening that works as an airway for the internal organs, is located near the end of its tail. Also, its butt is on the far side of its shell.
The nails on the front feet of a male turtle are long and wide at the base. These long nails are used to signal its intention to mate by touching the cheeks and shell of a female turtle. A male turtle also has a somewhat concave shell or plastron which is a perfect complement to the convex shape of a female turtle’s shell. Its long nails and concave shell are used in such a way that he stays in position during sexual contact.
A male turtle is generally smaller than a female turtle. Consequently, it also weighs less. Additionally, a male turtle is normally brightly colored to attract the opposite sex.
A female turtle, on the other hand, generally has short nails and tail. Its cloaca is located closer to its body. Its shell or plastron may be flat or a somewhat convex and its butt is not exposed. A female turtle is capable of laying eggs through mating with the opposite sex.
A female turtle can grow bigger than a male turtle and is, therefore, heavier. It also grows faster than the opposite sex.
FAQs
What Determines the Sex of a Turtle?
In most turtle species, the sex of the young is determined after the eggs have been fertilized. The temperature of the developing eggs determines the sex of each turtle. This is called “temperature-dependent sex determination,” or TSD.
Why are There More Female Turtles Than Males?
That’s a great question, and we have the answer! As our climate warms, the sex ratios of many turtle species will change. Warmer temperatures usually produce more female turtles. Over time, warmer temperatures could become a threat to some turtle species, such as the leatherback turtle.
If temperatures continue to increase, there won’t be enough male turtles to fertilize the females’ eggs. Eventually, there will only be female turtles, which could cause turtle populations to collapse over time.
Do Female Turtles Lay Eggs Even If They Don’t Mate?
Yes, female turtles can develop eggs even though they have not mated. But what’s interesting is that some female turtles can carry sperm for years. If they lay eggs, the eggs may be fertile and produce young.
What is Sexual Dimorphism in Turtles?
Sexual dimorphism is a term referring to differences between male and female turtles of the same species. This term is also used to describe the sexual differences between other types of animals. For instance, with turtles, the female is usually larger and heavier than the male.
Can You Tell a Turtle’s Sex by Its Eyes?
Some people say you can determine the sex of a turtle by the color of its eyes. They say some male turtles have red eyes. However, some female turtles also have red eyes, so eye color is not a good determinant when sexing turtles.
Male vs Female Turtles
What, then, is the difference between male and female turtles?
In terms of appearance, a male turtle is smaller and lighter than a female turtle. To attract females, a male turtle also has bright colors. A female turtle’s plastron is slightly convex, while a male turtle’s plastron is somewhat concave.
Additionally, a female turtle’s cloaca is near its body while a male turtle’s cloaca is near the end of its tail. Since it is the male turtle that signals the readiness to mate, it has longer nails on its forelegs so it can tap on the female turtle’s face and shell and hold her during mating. A male turtle’s butt is on the edge of its shell, while a female turtle’s butt is not exposed. A male turtle has a thick, long, and flat tail to contain its sex organ, while a female has a short tail. Female turtles are capable of laying eggs and male turtles are not.





