In science, the term “molecule” is used to refer to a group of atoms bonded together. The molecules are classified into two groups: molecular and ionic compounds. In this article, we will discuss the ionic and molecular compounds, the difference between them, and the properties of ionic and molecular compounds.
Summary Table
| Ionic Compound | Molecular Compound |
| The ions present in the ionic compounds are held together by electrostatic forces of attraction. | The compounds present in the molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds. |
| The metallic ions present in the ionic compounds are usually present in their charged state. | The non-metallic atoms like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon and chlorine are present in the molecular compounds. |
| Ionic compounds have a high melting point. | Molecular compounds do not have an exact melting point |
Definitions

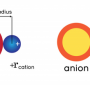
An ionic compound is a substance that consists of positively charged ions and negatively charged ions. The positive and negative ions are held together by the attraction between them. The ions can be positive or negative depending on the number of electrons present in them. If an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion called cation. If an atom gains one or more electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion called anion. In an ionic compound, the cations and anions are held together by electrostatic forces of attraction (or repulsion).
Ionic compounds have high melting points. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when melted or dissolved in water. Ionic compounds dissolve well in water to form electrolytes. Ionic compounds have high boiling points and low density compared to other substances such as molecular compounds. They also have high conductivity compared to molecular compounds due to their ability to conduct electricity.
Ionic Compounds examples include NaCl (sodium chloride), NaClO (sodium hypochlorite), CaF 2 (calcium fluoride), NaNO 3 (sodium nitrate), Na 2 SO 4 (sodium sulfate), CaSO 4 (calcium sulfate), FeCl 3 (iron(III) chloride), KNO 3 (potassium nitrate), and MgCO 3 (magnesium carbonate).
A molecular compound is a substance composed of molecules. The molecules are made up of atoms and the compounds have covalent bonds between the atoms. In a molecular compound, the electrons are shared by two or more atoms and there is no free electron in the molecule. For example, H 2 O (water), CH 4 (methane), N 2 (nitrogen) etc. are examples of molecular compounds.
Molecular compounds are neutral, as they have an equal number of positive and negative charges. Molecular compounds also have no color. In molecular compounds, the atoms are tightly bonded and there is no free electron in the molecule. Therefore, molecular compounds are non-conductors of electricity.
Molecular compounds do not have a definite melting point and boiling point. When the temperature is increased, the molecules move faster and faster. When the temperature reaches a certain level, there is a phase change. This means that the molecular compound changes from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas. Molecular compounds are also non-volatile. This means that they do not evaporate easily. The molecular compounds are very stable.
The formula of molecular compounds is given by the ratio of atoms present in the compound. For example, H 2 O (water) has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The formula of water is H 2 O.
Ionic vs Molecular Compound
The ionic and molecular compounds are two types of compounds that are present in the solid state. The difference between them is that the ions present in the ionic compounds are held together by electrostatic forces of attraction. The compounds are formed by the combination of metal and non-metal atoms. The metallic ions present in the ionic compounds are usually present in their charged state.
The ions present in the ionic compounds have a fixed valence and each type of metal atom can only form a specific number of ions. For example, sodium forms one ion, potassium forms two ions, etc. The number of atoms present in an ion is called valence of the metal atom. For example, the valence of sodium is 1, that of potassium is 2 and so on.
The compounds present in the molecular compounds, however, are held together by the covalent bonds. The non-metallic atoms like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon and chlorine are present in the molecular compounds. The covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of electrons between the atoms.
The ions present in the ionic compounds have a fixed charge and can only be obtained in their charged state. The charged ions can easily move from one place to another because of their high mobility. This is why ionic compounds have a higher melting point than molecular compounds. For example, NaCl has a melting point of 801oC while water has a melting point of 0oC.
The compounds present in the molecular compounds are not in their charged state. The neutral molecules are less mobile than the charged ions. This is why the molecular compounds have a lower melting point than ionic compounds. For example, H 2 O has a melting point of 0oC while NaCl has a melting point of 801oC.
How to identify ionic and molecular compounds?
There are a few ways to identify ionic and molecular compounds. One of the most common ways is to check the melting point of the compound. You can also identify the compound by checking the conductivity of the compound. Ionic compounds are more conductive than molecular compounds. Also, Ionic compounds are generally hard and brittle.
Should you be using ionic or molecular compounds?
Both ionic and molecular compounds are very important in science. They are used in a wide range of applications. For example, they are used in the preparation of polymers, medicines, batteries, water treatment plants and so on. The ionic compounds are also used to prepare soft drinks like cola. However, the most important application of ionic compounds is in their ability to transfer electrical energy. The batteries that are used in automobiles and smartphones use ionic compounds to transfer electrical energy.