Medical issues are always scary.
Even more so when you hear about a possible staph or strep infection! You don’t even know which one is worse, so you fear both of them. Let’ see whether you are right in doing so. Keep reading to find out what is the difference between staphylococcus and streptococcus.
Summary Table
| Staphylococcus | Streptococcus |
| A grape-shaped bacteria | A chain-shaped bacteria |
| Has multiple axes cellular division | Forms around a single axis |
| There are 30 species | There are 50 species |
| There is one group | There are three different groups |
| Typically found on the skin | Typically found in the ear, nose and throat areas |
Descriptions
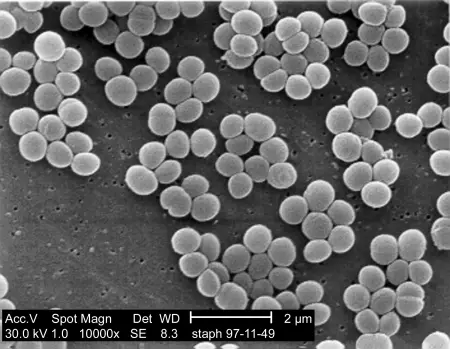
Staphylococcus is a group of bacteria responsible for a number of infectious diseases. The name is of Greek origin and it means staphyle = grapes, and kokkos = berry. This best describes the aspect of the bacteria. There are over 30 species of Staphylococcus, of which Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of infection.
They can either affect a part of the body or the bloodstream. Some staph infections can be left untreated, having the body take care of itself, while others require medical intervention such as cleaning the infected area, draining possible puss accumulation, and even taking medication to destroy the bacteria.
This bacteria lives on the skin. As long as the natural protective layer of the organism is not damaged, the bacteria causes no harm. However, should you cut the skin or create access to bacteria any other way, staph infections become possible. A person can be resistant to such infections or can have a weakened immune system and not react in due time to infection. These infections are only contagious if a healthy person comes into contact with contaminated items such as wound bandages, bed clothing, razors, and other moisture-based transmission objects. In this case, there is an incubation period of 4 to 10 days.
Apart from the damage caused by their presence alone, Staphylococci can also produce harmful toxins.
This is the case for most food poisoning cases.
In the case of local infections, such as infected wounds, a staph infection will cause pain, redness, and swelling. When it enters the bloodstream, it causes fever, chills, and low blood pressure.
In the case of severe staph infection, death can occur. This is mainly the case of burn victims and of people whose wounds have allowed bacteria to invade in great numbers.
Antibiotics are used to fight off staph infections. The way the body reacts to antibiotics depends on how exposed it has been to such substances and on the strain of the infection. A person who has taken a lot of antibiotics in the past may not respond to treatment with milder drugs.
Also, there is a strain of resistant bacteria, called MRSA, that is resistant to many types of antibiotics.
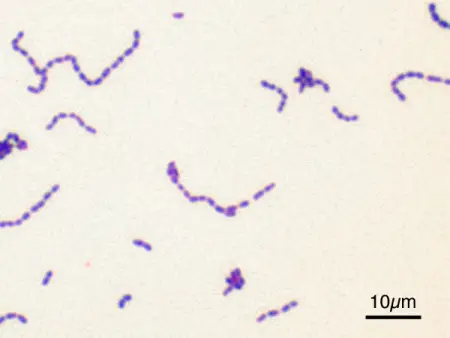
Streptococcus is a group of bacteria that cause a wide range of diseases. The Greek name refers to their chain shaped form, as this bacteria multiplies by division along a single axis, hence their chain shape. There are over 50 species in this genus, each responsible for a different type of disease.
More importantly, there are three different groups of Streptococcus:
- group A – dispersed by infected hosts, inhaled by healthy individuals
- group B – already existing on a woman’s body, transmitted to babies during vaginal delivery
- group C – bacteria that inhabit the human body and that can, at times, trigger infections
Group A Streptococci can infect the ear, nose and throat, skin, and other parts of the body. They are the cause of pneumonia, pleurisy, scarlet fever, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, heart valve infection, rheumatic fever, and kidney inflammation.
Symptoms of a strep infection vary according to the infected area and to the type of infection. You can have localized soreness which is caused by a skin wound that has been infected or even necrotizing fasciitis. Fever and even shock can be an accompanying symptom if the infection is strong and the body has a proportionate reaction.
The most common form of Streptococcus infection is the strep throat. This may seem like a light infection and a simple sore throat, but antibiotic treatment is necessary to cure it. A strep throat is easy to recognize by:
- difficulty breathing
- difficulty swallowing
- a sore throat for more than two days
- red spots on the tonsils and in the back of the mouth
- headache
- chills
- sudden and very high fever
- swollen lymph nodes in the neck
Antibiotics such as penicillin and amoxicillin are recommended in these cases, and it is imperative that the treatment is completed by the patient. Lack of treatment can result in complications such as the spread of the infection to more sensitive and hard-to-treat areas.
Staphylococcus vs Streptococcus
The main difference between them is in how they look. The Staphylococcus has multiple axes cellular division, which results in its grape-like shape. On the other hand, Streptococcus forms around a single axis, resulting in its chain-like shape.
Also, while there are over 30 species of Staphylococci and over 50 species of Streptococci, only the latter is also divided into three separate groups, depending on the substances used to trace them.
Although doctors need to test to check the presence of either a staph or a strep infection, there are specific places where either one is more prone to be found. A staph infection is more likely to affect skin wounds, whereas a strep infection is more likely to affect the ear, nose, and throat areas.