It is very important to follow grammar rules to communicate effectively. One of the many parts of speech that adds meaning to a sentence is the verb tense. When verb tense is used incorrectly, sentences sound very confusing!
Verb tenses do not only apply to action verbs. Linking verbs, like “is” and “are,” also have past forms, which are “was” and “were,” respectively. These verbs are not interchangeable as their usage depends on the subject. This article will discuss the difference between the two.
Summary Table
| Was | Were |
| Past tense of “is” | Past tense of “are” |
| Used with singular and uncountable nouns or pronouns | Used with plural nouns and pronouns |
| Follows the pronoun “I” if the statement talks about a fact | Paired with the pronoun “I” if it is in a subjunctive mood or if the statement expresses something not real or hypothetical |
Definitions
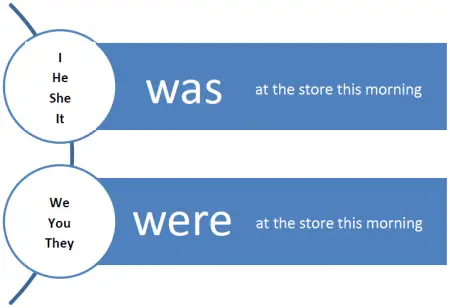
The verb was is the past tense of the verb “is.” It is used with:
- Singular nouns. For example: The test was really easy!
- First person singular pronouns. For example: I was watching TV when you called.
- Third person singular pronouns. For example: It was very nice to see you at the party last night.
- Singular indefinite pronouns (everybody, anybody, somebody, everyone, anything, everything, something). For example: Everyone was so kind and helpful.
- Singular countable quantifier pronouns. For example: Well, one was able to get away.
- Uncountable quantifier pronouns (enough, little, less). For example: Little was known about the life of Edward Smith.
On the other hand, the verb were is the past tense of the verb “are.” It is used with:
- Second person singular and plural. For example: Were you happy with the results?
- First person plural. For example: We were tired of waiting, so we left.
- Third person plural. For example: They were so rude to that poor guy.
- Plural indefinite pronouns. For example: Both were lovely!
- Plural countable quantifier pronouns (few, many, more). For example: Many were against it.
It is important to note, however, that the pronoun “I” uses the verb “were” if it is used in the subjunctive mood, or in statements that are not real or are hypothetical. For example:
- If I were the President of the United States, I’d give homes to all people living on the street. (unreal statement)
- I wish I were in New York! (expresses what I wish to happen)
- I’d be a model if I were taller! (hypothetical statement)
Was vs Were
What, then, is the difference between was and were?
“Was” is the past tense of “is” while “were” is the past tense of “are.” The verb “was” is generally used for singular and uncountable subjects, both nouns and pronouns. On the contrary, the verb “were” is used when the subject is plural.
Additionally, the verb “were” should be used with the pronoun “I” if it is used in a subjunctive mood, or if the statement talks about something that is not real or just hypothetical. “I” should be paired with “was” if the statement talks about a fact.
Is It “If I Was” or “If I Were”?
As a general rule, in simple past tense, was is used for singular subject and were for plural.
For example, I was going to school and we were going to the park.
However how to use “If I were” or “If I was” is a classic English grammar debate. This grammar rule may seem complicated for non-English speakers at first, but if you remember the know how, you’ll always get it right!
Use were after “I” to express a hypothetical statement, subjunctive mood or an assumption about something that might have happened in the past. It expresses an opinion or speculation on something that could have happened in the past but did not happen because it did not occur in reality. In other words, if you were something else in the past, then this would be what you would have been like. For example:
If I were a rich man, I would be building a house right now.
This sentence may seem strange to some people because “I was” seems to be the correct choice. But in this sentence, you are imagining a hypothetical situation or talking about things that are contrary to fact.
Use were after “I” when you can follow each statement with “But I’m not.” This is the easiest way to tell whether you may be using if I were correctly.
Another examples of hypothetical situation statements are given below:
Example 2: If I were you, I would definitely do this instead of that.
Example 3: If I were you, I would probably go on a holiday with my family this year.
Example 4: If I were you, I would take advantage of these opportunities and use them to our advantage.
Example 5: If I were an actress, I would I would be on Broadway right now.
When to Use If I Was?
Use was after “I” in conditional sentence when you are talking about something that actually happened. For example, “If I was late for class when I was a teenager, my teachers grounded me.” Another example, “I apologize if I was not clear enough”.
In those sentences, each sentence is true.
To decide whether you should use was or were; first, you should determine if the thing you are talking about is something that actually happened or something that you are imagining may be happened.
If it really happened, use “if I was.”
Was vs Were in Passive Voice
In English, there are two kinds of sentences: active and passive. Active sentences have a subject and an object, and the verb describes the action.
Passive sentences don’t have a subject or an object, and the verb describes the state of being rather than the action itself.
Active voice sentences are usually short and to the point. They are often good writing, but they are also sometimes boring.
Passive voice sentences are usually long and wordy. They are often good writing, but they can be hard to understand as well.
There is a trade-off between readability and accuracy in both cases, although there is a difference between the two.
But the verbs ‘was’ or ‘were’ don’t automatically suggest that the sentences are passive voice. We create passive voice by pairing a conjugation of ‘to be’ with a past participle of a different helping verb.
Let’s look at an example:
“The ball was hit by Jones yesterday.” (a passive voice).
“Jones hit the ball yesterday.” (an active voice).
“My sister cleaned the house last night.” (an active voice).
“The house was cleaned by my sister last night.” (passive voice).
“The house was clean and tidy.” (an active voice).
“The teacher answered my questions.” (an active voice).
“My questions were answered by the teacher).” (passive voice).
Examples paragraph using was and were
When I was young, I used to play with my friends in the park. I was the only girl there and it was fun. Sometimes, my friends would give me things to do for them.
If they did, I would take the things back after they were done with them.
This always made me feel very important because I was important to my friends.
One day, I was playing with my friends in the park and I saw a girl who was smaller than me. I went up to her and asked her if she wanted to play with us.
She said yes and we played together for a while. After that, I played with her a lot. She was a very nice girl and I was happy to play with her. She never asked me for anything.
I liked playing with her because she never made me feel like I was too important to her.
One day, she went home and I went back to playing with my friends in the park. I didn’t see her for couple weeks after that.
When I got there, they told me that she moved to another state. It made me feel sad when they told me this because she was my friend and I missed her very much.





