People often use either a VPN or a Proxy as a form of privacy protection when accessing content on the web. However, each technology uses a different way of masking a user’s identity online. Let’s highlight their features and find out what’s different between the two.
Summary Table
| VPN | Proxy |
| Allows secure user access to private network | Allows users to access resources from other networked servers |
| Installed at the operating system level | Acts as middleman for a single application in a device |
| Encrypts data | Does not encrypt data |
Definitions
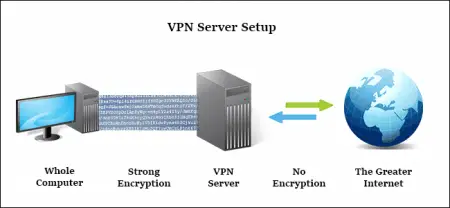
A VPN, or a virtual private network, allows a user to access a private network using a public network (e.g. the internet). It provides the security of being able to safely send and receive data in a private network while using a less secure public or shared connection. VPNs also provide a level of management and functionality of a private network in connected devices. Although online connections can never be totally anonymous, VPNs help increase a user’s security and privacy when accessing the web.
Corporate employees can safely access a company’s intranet while being outside the office using a VPN as well. A business organization employing remote staff from anywhere in the globe can securely connect to their dedicated network. A VPN can also be used by individual users as a work-around for location-based restrictions and censorship in the internet. Wireless transactions can be safely conducted when using a virtual private network.
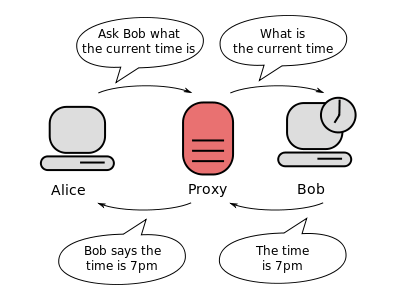
A proxy, or a proxy server, can either be an application or a computer system that handles requests from other networked devices looking to access resources from other servers. Web proxies are commonly used by individuals seeking access to web content hindered by regional locks, or even parental locks. It is also usually used to provide a level of online anonymity by hiding the user’s IP address. Proxies are used to filter user uploads and downloads as well as screen web content
For example, a user in Australia is unable to access web content intended for American users. By using a web proxy based in the US, he is able to mask his IP address, and thus can easily gain access to the website that screens web traffic other than those in the US. However, web proxies cannot encrypt communications (traffic) between them and the users. Thus, anyone who can intercept that traffic (e.g. your internet service provider, hackers) can determine any user identity.
VPN vs Proxy
So what’s the difference between a VPN and a proxy? While both allow users to appear as if they’re accessing web content from a different location, the manner in which it is done, including the level of privacy they offer, varies.
A VPN is a secure network made accessible through a public network such as the internet. It is typically used by organizations to allow employees safe access to their company intranet. A web proxy, on the other hand, serves as a “middleman” that accepts requests from other computers to access services or resources from other servers. A VPN offers a high level of security as the flow of data between the private network and its users are encrypted. A proxy server, however, does not provide data encryption. A VPN is installed in the operating system, and thus all active applications in the device can be monitored. A proxy server only acts as an intermediary for a single application (e.g. torrenting apps, web browser).
Video
Here’s a YouTube video showing more about the difference between VPNs and proxy servers.